The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is stored on the motherboard inside a computer’s case. It is a critical component responsible for processing instructions and managing the operation of the computer.
The CPU is stored on the motherboard inside a computer’s case. It fits into a specific socket designed for its type. In mobile devices, the CPU is integrated into the mainboard.
In this article, we will discuss “where is the cpu stored”.
Understanding The CPU:
What Is A CPU?
A CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the main component of a computer that processes instructions and manages tasks. It performs calculations and runs programs, making it essential for the computer’s operation. The CPU is often called the “brain” of the computer.
What Are The Functions Of The CPU?
The CPU performs several key functions in a computer. It executes instructions from programs, processes data, and manages tasks.
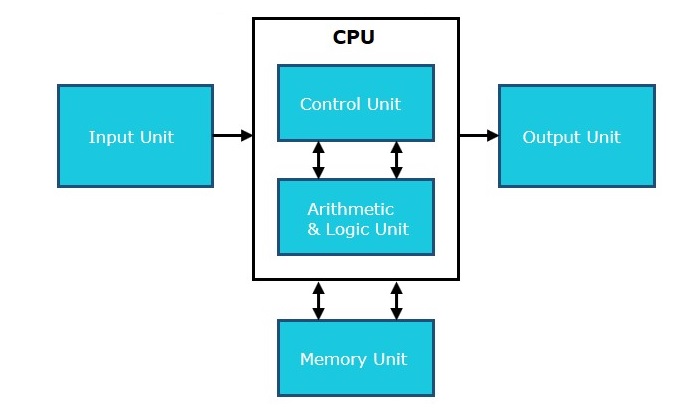
It also controls other components, ensuring they work together smoothly. The CPU handles calculations, logic operations, and data transfers, making it essential for running software and operating systems.
Read : Question About % CPU From Top Command – A Complete Guide Of 2024!
Where Is The CPU Located?
Desktop and Laptop Computers:
The CPU is found on the motherboard inside the case. It’s installed in a special socket, usually under a cooling fan or heatsink.
Smartphones and Tablets:
In mobile devices, the CPU is built into the mainboard and is not removable. It’s small and designed for efficient performance and battery life.
Connection to Other Parts:
The CPU connects to the motherboard through its socket. It communicates with other parts like RAM and storage to process data quickly.
Cooling System:
CPUs in computers usually need cooling fans or heatsinks. These help to keep the CPU cool while it works to avoid overheating.
Where Is The CPU Stored?
The CPU is stored on the motherboard inside the computer case. In desktops and laptops, it fits into a specific socket on the motherboard. In mobile devices like smartphones and tablets, the CPU is integrated into the mainboard. The CPU’s location is crucial for cooling systems, upgrades, and replacements.
Where Does The CPU Store Its Computations?
The CPU stores its computations in a few key places. First, it uses registers inside the CPU for quick access to data while processing. Then, it stores frequently used data in the cache memory (L1, L2, and L3) to speed up tasks.
Finally, for larger storage, the CPU uses the computer’s RAM (Random Access Memory) to hold temporary data while working. Once the CPU finishes, the data may be saved to storage devices like a hard drive or SSD for long-term use.
CPU Socket And Motherboard:
CPU Socket: The CPU socket is a special connector on the motherboard where the CPU is installed. It provides the electrical interface between the CPU and the motherboard, allowing the CPU to communicate with other components.
Motherboard Layout: The motherboard is the main circuit board of a computer. It houses the CPU socket, RAM slots, and other essential components, providing pathways for data to travel between the CPU and other parts of the computer.
What Are The Different Types Of CPUs?
Desktop CPUs:
These are designed for desktop computers and offer high performance. They typically have more cores and higher clock speeds compared to other types.
Laptop CPUs:
Optimized for portable devices, laptop CPUs balance performance with energy efficiency to extend battery life while providing adequate processing power.
Mobile CPUs:
Found in smartphones and tablets, these CPUs are compact and energy-efficient to fit into small devices and maximize battery life. They are integrated into the mainboard to save space.
CPU Cooling Systems:
- Desktop CPUs: High-performance processors used in desktop computers, often with higher clock speeds and more cores.
- Laptop CPUs: Designed for energy efficiency and compact size, balancing performance with battery life.
- Mobile CPUs: Integrated into smartphones and tablets, focusing on low power consumption and space-saving.
Read : Very High CPU Load, But Nothing Significant In Top – Ultimate Guide 2024!
CPU Upgrades And Replacements:
Upgrading or replacing a CPU involves removing the old one from its socket on the motherboard and installing a new one. Ensure compatibility with your motherboard and cooling system. For laptops, upgrades are often limited due to soldered CPUs.
What Is The Main Store Of The CPU?
The main storage of the CPU is its internal cache, which includes L1, L2, and L3 caches. These caches store frequently accessed data and instructions to speed up processing. For larger storage, the CPU relies on the computer’s RAM and hard drive.
Where Does The CPU Sit In The Computer?
The CPU sits on the motherboard inside the computer case. It is mounted in a specific socket and often covered by a cooling system, such as a fan or heatsink, to manage its temperature.
How Do You Locate Your CPU?
To locate your CPU, open the computer case and look for the motherboard. The CPU will be installed in a specific socket on the motherboard, usually covered by a heatsink or fan. In laptops, accessing the CPU may require removing the bottom panel.
Where Do I Find My CPU Memory?
CPU memory, or cache, is located on the CPU itself, not on the RAM. For CPU cache, check the processor specifications. RAM, which also affects performance, is found in slots on the motherboard, usually accessible by opening the computer case.
What Is The Temporary Storage Location Inside The CPU?
The temporary storage location inside the CPU is called the cache. It includes L1, L2, and L3 caches, which store frequently accessed data and instructions to speed up processing and improve performance.
How Are Processor Instructions Stored In RAM?
Processor instructions are stored in RAM as part of the system’s memory. When a program runs, its instructions are loaded from storage into RAM, where the CPU can quickly access and execute them, improving overall performance and speed.
Read : CPU On Ubuntu Running High – GPU – A Complete Guide Of 2024!
Where Does The CPU Store Its Computations?
The CPU stores its computations in its internal registers and cache memory. Registers hold immediate data and instructions, while cache memory stores frequently accessed information to speed up processing. For long-term storage, data is saved to RAM or storage drives.
What Is Data Storage?
Data storage refers to the process of saving digital information, such as files, documents, and programs, on various storage media. This includes hard drives, SSDs, RAM, and cloud storage, allowing data to be retrieved and used by computers and devices.
How Does The CPU Work Step By Step?
The CPU works in several steps: it fetches instructions from memory, decodes them to understand what needs to be done, executes the instructions by performing calculations or data operations, and then writes the results back to memory or outputs. This cycle repeats continuously to run programs and manage tasks.
Read : High CPU Usage During Disk Io? Is This Normal? – Enhance Efficiency 2024!
Frequently Ask Questions:
Can The CPU Be Moved To Another Computer?
Yes, if the new computer’s motherboard supports the same CPU type.
Is The CPU Easily Accessible In A Desktop Computer?
Yes, it is accessible by opening the computer case and removing the heatsink.
Why Is The CPU Important For A Computer?
It processes instructions and manages tasks, making it essential for computer operation.
Does The CPU Location Affect Computer Performance?
The CPU’s location does not affect performance, but proper cooling is crucial.
Can I Replace A Laptop CPU Myself?
No, replacing a laptop CPU yourself is usually challenging due to its integration and soldering. It often requires professional help and may involve significant disassembly or special tools.
Are All CPUs The Same Size?
No, CPUs come in different sizes and shapes, depending on their type and the device.
How Can I Tell If My CPU Is Overheating?
Overheating can cause slow performance, random shutdowns, or unusual fan noise.
Do Tablets Have Removable CPUs?
No, in tablets, the CPU is typically soldered onto the mainboard and is not removable.
Is The CPU Stored In The Same Place In All Computers?
The CPU is stored on the motherboard in all computers, but its mounting and accessibility can vary.
Can I Upgrade My CPU Without Changing Other Components?
No, upgrading your CPU typically requires a compatible motherboard and may need a new cooling system. Check if other components like RAM and power supply are also compatible.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the CPU is a vital component in any computer, located on the motherboard or integrated into the mainboard of mobile devices. Understanding its placement helps in maintaining and upgrading your system. Proper cooling and compatibility checks are essential for optimal performance and longevity.
Related Posts:
- CPU Machine Check Architecture Error Dump – Fix Hardware Issues!
- Why Is My CPU Overclocking Itself – Optimize Your Performance!
- CPU Usage Drops When I Open Task Manager – Optimize Your Performance!
- What Is Hammering The CPU When Top Is Not Running? – Upgrade Your Knowledge Today!
