I experienced high CPU usage during disk I/O on my older laptop. After updating drivers and adding more RAM, the issue improved significantly. It taught me that hardware upgrades and software optimization are crucial for better performance.
High CPU usage during disk I/O can be normal, especially during intensive tasks like file transfers or backups. However, it can also indicate issues like outdated drivers, insufficient RAM, or hardware imbalances that may need addressing.
Wondering if high CPU usage during disk I/O is normal? It can be, especially during heavy tasks, but it might also signal hardware or software inefficiencies. Let’s dive deeper!
Is High CPU Usage During Disk I/O Typical Or Indicative Of Underlying Issues?
High CPU usage during disk I/O can be typical under heavy workloads like large file transfers or database operations. However, persistent high usage could indicate inefficiencies like outdated drivers, software bugs, or insufficient hardware.
Monitoring and optimizing system performance is crucial to ensure efficient operations and identify underlying issues for smoother functionality and enhanced productivity.
Does CPU Affect Disk Io?
Yes, the CPU directly affects disk I/O performance. The CPU manages data transfer between memory and storage devices, orchestrating read and write operations.
A powerful CPU can process data faster, reducing latency in accessing and manipulating data on disks.
How Do I Fix 100% CPU And Disk Usage?
- Identify The Cause: Use Task Manager (Windows) or Activity Monitor (macOS) to find which processes are consuming the most CPU and disk resources.
- Update Software: Ensure your operating system and all applications are up-to-date to fix bugs and improve performance.
- Check For Malware: Run a full system scan using antivirus software to detect and remove any malware that could be causing high CPU and disk usage.
- Disable Startup Programs: Disable unnecessary programs from starting up with your computer to reduce CPU and disk load.

- Update Drivers: Update device drivers, especially for your graphics card and storage devices, to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.
- Adjust Power Settings: Change power settings to ‘High Performance’ to allocate more resources to your CPU and disk for better performance.
- Clear Temp Files: Use disk cleanup tools to remove temporary files and free up disk space, which can reduce disk usage.
- Check For Background Processes: Close or disable unnecessary background processes and services that are consuming CPU and disk resources.
- Defragment Hard Drive (if HDD): If using a hard disk drive (HDD), defragment it to optimize data storage and improve disk performance.
- Upgrade Hardware: Consider upgrading your hardware, such as adding more RAM or switching to a solid-state drive (SSD), to improve overall system performance.
Why Is My CPU Idling So High?
- Background Processes: Several background apps or services running simultaneously can keep the CPU active even when you’re not actively using the computer.
- Malware or Virus: Malicious software can run hidden processes that consume CPU resources.
- Outdated Software: Older applications or drivers may not be optimized for efficiency, causing higher CPU usage.
- High System Load: Running many applications or tasks simultaneously can keep the CPU busy, even if they’re not actively being used.
- Power Settings: Inappropriate power settings, like ‘High Performance’, can keep the CPU running at higher speeds even when it’s not necessary.
- Heat Issues: Overheating can cause the CPU to throttle, maintaining high idle usage to manage temperature.
- Windows Updates: Background updates or maintenance tasks by the operating system can increase CPU usage temporarily.
- Hardware Issues: Faulty hardware components, such as a failing CPU fan or power supply, can cause the CPU to run at higher idle levels.
Why Is My CPU Usage So High Randomly?
High CPU usage randomly can stem from background processes, scheduled tasks, or resource-demanding applications running unexpectedly.
Malware, outdated software, or system updates can also cause spikes. Monitoring task managers for culprit processes and ensuring software and drivers are up-to-date can help identify and mitigate these issues.
Is It Normal To Have High CPU Usage?
High CPU usage can be normal during intensive tasks like gaming, video editing, or software compiling.
However, sustained high usage without such activities may indicate inefficiencies or issues like background processes, malware, or outdated software.
Monitoring and optimizing CPU usage ensures smooth performance and prevents unnecessary strain on the system.
Is 20% CPU Usage Idle Bad?
No, 20% CPU usage at idle is generally not considered bad. It indicates that a portion of the CPU’s processing power is being used by background tasks or system processes.
This level of usage suggests the CPU has the capacity for additional tasks without impacting performance significantly.
Is A CPU Idle At 40?
A CPU idle at 40 typically refers to 40% idle usage, meaning 60% of the CPU’s processing capacity is actively engaged.
This level of idle usage suggests moderate activity, with ample processing power available for additional tasks or spikes in demand without experiencing performance bottlenecks.
What Is Normal CPU Usage At Idle Windows 10?
Normal CPU usage at idle on Windows 10 typically ranges from 0% to 10%. This indicates that the system is not actively running intensive processes and is operating efficiently. Higher idle usage could suggest background tasks or applications using resources.

What Should My CPU Be Running At Idle?
Your CPU should ideally be running at idle between 0% to 10% on average. This range indicates that your system is efficiently managing background processes and is ready to handle additional tasks without experiencing performance issues or slowdowns.
What Is A Bad CPU, Idle Temp?
A bad CPU idle temperature is typically above 50°C (122°F). Higher temperatures can indicate inadequate cooling, improper thermal paste application, or dust buildup, potentially leading to overheating and reduced CPU lifespan. Optimal cooling ensures stable performance and longevity.
What Is The Relationship Between CPU And Io?
- Processing Instructions: The CPU executes instructions, including those related to reading from or writing to storage devices.
- Data Transfer: The CPU manages data transfer between memory and storage devices, initiating and controlling I/O operations.
- System Bus: I/O operations use the system bus to transfer data between the CPU, memory, and peripherals like disks.
- Interrupt Handling: When I/O devices need attention (e.g., completing a read/write operation), they send interrupts to the CPU, which then handles these requests.
- CPU Utilization: Heavy I/O can impact CPU performance if the CPU spends significant time waiting for data transfers to complete.
- Hardware Interface: The CPU communicates with storage devices through interfaces like SATA, NVMe, or USB, each affecting data transfer speeds and latency.
Why Do I Have High CPU Usage When Not Doing Anything?
Background Processes:
- What Happens: Various applications and system processes run in the background, performing tasks like updates, syncing, or system maintenance.
- Why It Matters: These can consume CPU resources even when you’re not actively using the computer.
Malware Or Viruses:
- What Happens: Malicious software can run hidden processes that use significant CPU power.
- Why It Matters: Malware can severely impact system performance and pose security risks.
Outdated Software:
- What Happens: Old or poorly optimized software and drivers can cause inefficiencies, leading to higher CPU usage.
- Why It Matters: Updating software ensures better performance and security.
Windows Updates And Maintenance:
- What Happens: Windows may run updates, indexing, or other maintenance tasks in the background.
- Why It Matters: These tasks are essential but can temporarily spike CPU usage.

System Configuration Issues:
- What Happens: Incorrect settings, such as power plans set to high performance, can keep the CPU running at higher speeds.
- Why It Matters: Proper configuration can help reduce unnecessary CPU usage and extend hardware life.
What Is The Idle CPU Cycle?
The idle CPU cycle refers to the periods when the CPU isn’t executing active tasks and is waiting for instructions.
These cycles indicate system efficiency, as the CPU conserves energy and prepares to handle new processes swiftly.
How Do I Lower My CPU Idle?
- Close Background Apps: Shut down unnecessary programs.
- Update Software: Ensure all software and drivers are up-to-date.
- Adjust Power Settings: Opt for balanced or power-saving modes.
- Monitor Startup Programs: Disable apps from launching at startup.
How Do I Reduce CPU Idle Time?
- Multitask Efficiently: Streamline processes to minimize downtime.
- Utilize Background Tasks: Engage in productive activities during idle moments.
- Optimize System Settings: Adjust power plans for balanced performance.
- Monitor Resource Usage: Identify and mitigate unnecessary CPU drains.
What Is Normal CPU Idle?
Normal CPU idle typically ranges from 0% to 10%. This indicates that the CPU is not actively processing tasks and is efficiently managing background operations.
Higher idle percentages may indicate background processes or applications using system resources.
What Command Can You Use To Show CPU Idle Time?
To show CPU idle time in many operating systems, including Linux and Unix-like systems, you can use the top command.
In Windows, you can use Task Manager or the System Monitor tool to view CPU idle time as a percentage of total CPU usage.
Why Is My CPU Usage So High At Idle?
High CPU usage at idle can result from background processes like updates, antivirus scans, or faulty drivers. Malware or outdated software can also contribute.
Checking Task Manager or Activity Monitor helps identify which processes are consuming CPU resources, aiding in troubleshooting and optimization efforts.
How Is CPU Idle Time Calculated?
CPU idle time is calculated as a percentage of total time. It represents the proportion of time the CPU is not actively executing tasks.
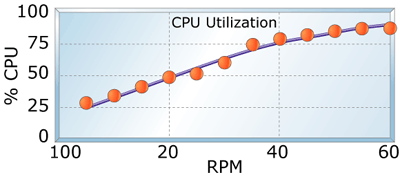
This value is derived from the difference between 100% and the sum of time spent on user, system, and interrupt processes.
Frequently Ask Questions:
1. Why Is My Cpu Usage So High Randomly?
Randomly high CPU usage can occur due to background processes, malware, outdated software, system updates, or hardware issues, all of which can temporarily spike CPU utilization beyond normal levels.
2. Why Is The Cpu Idle During Io?
The CPU may idle during IO operations because it delegates data transfer tasks to dedicated controllers and hardware, allowing it to handle other tasks or conserve power until needed for processing the next set of instructions.
3. How Do I Fix High CPU Usage On Idle?
To fix high CPU usage at idle, check for background processes consuming resources and close unnecessary applications or services running in the background. Updating software and drivers can also help optimize CPU performance.
4. Why The Cpu Would Be Idle?
The CPU would be idle when there are no active tasks requiring processing, allowing it to conserve power and remain ready to handle new instructions or tasks as they arise without unnecessary energy consumption.
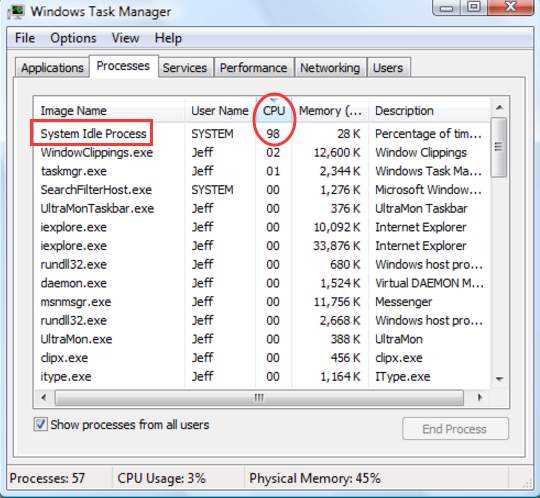
5. What Is The System Idle Process In CPU Utilization?
The System Idle Process in CPU utilization represents the percentage of time the CPU is not actively executing tasks. It essentially reflects the idle time of the CPU, indicating how much capacity is available for processing new tasks.
6. What Cpu Usage Is Considered Idle?
CPU usage is considered idle when it is low, typically ranging from 0% to 10%. This indicates that the CPU is not actively processing tasks and is available for new instructions without a significant workload.
7. Which Operating System Reduces CPU Idle Time?
Operating systems like Linux, macOS, and Windows manage CPU idle time through power management features that optimize CPU usage based on workload, reducing idle time to improve efficiency and performance.
8. How Do I Reduce Cpu Idle Temperature?
To reduce CPU idle temperature, ensure adequate cooling by cleaning dust from cooling fans, applying fresh thermal paste between the CPU and heatsink, and adjusting fan speeds in BIOS settings for optimal airflow.
9. What Cpu States Are Idle?
The CPU states that are idle include the “C0” state where the CPU is actively processing tasks and the “C1” state where it is idle and waiting for instructions.
10. What Happens When The Computer Is Idle For A Long Period?
When a computer is idle for a long period, power-saving features kick in to reduce energy consumption, such as dimming the screen, spinning down hard drives, or putting the CPU into lower power states to conserve energy.
Conclusion:
In Conclusion, High CPU usage during disk I/O can be a common occurrence during tasks like large file transfers or backups. However, persistently high usage might indicate underlying issues such as outdated drivers or insufficient hardware. Optimizing your system through updates, checking for malware, and adjusting settings can greatly improve performance.
