When I first built my PC, I wasn’t sure how much RPM my CPU fan needed. After some testing, I found that keeping it around 1500 RPM worked well for regular tasks. For gaming or heavy use, I let it go up to 2500 RPM to keep temperatures low and prevent overheating.
The ideal RPM for a CPU fan usually ranges from 1000 to 2500 RPM. For normal tasks, 1000 to 1500 RPM is enough. If you’re gaming or doing heavy work, you may need 2000-2500 RPM for better cooling. Always check your CPU temperature to adjust the fan speed accordingly.
Stay tuned as we discuss “How Much RPM for CPU Fan” and the ideal speeds for optimal performance and cooling.
What Is RPM in a CPU Fan?
RPM in a CPU fan means “revolutions per minute.” It shows how many times the fan spins in one minute. A higher RPM means the fan spins faster, which can cool the CPU better. Lower RPM fans are quieter but may not cool as much. RPM helps you know how well the fan is working to keep your computer safe from heat.
Why Does CPU Fan RPM Matter?
CPU fan RPM matters because it controls the cooling of the CPU. If the RPM is too low, the CPU might get too hot, causing slow performance or even damage. On the other hand, very high RPM can make the fan noisy. Keeping the right RPM helps balance cooling and noise, keeping the computer safe and running smoothly.
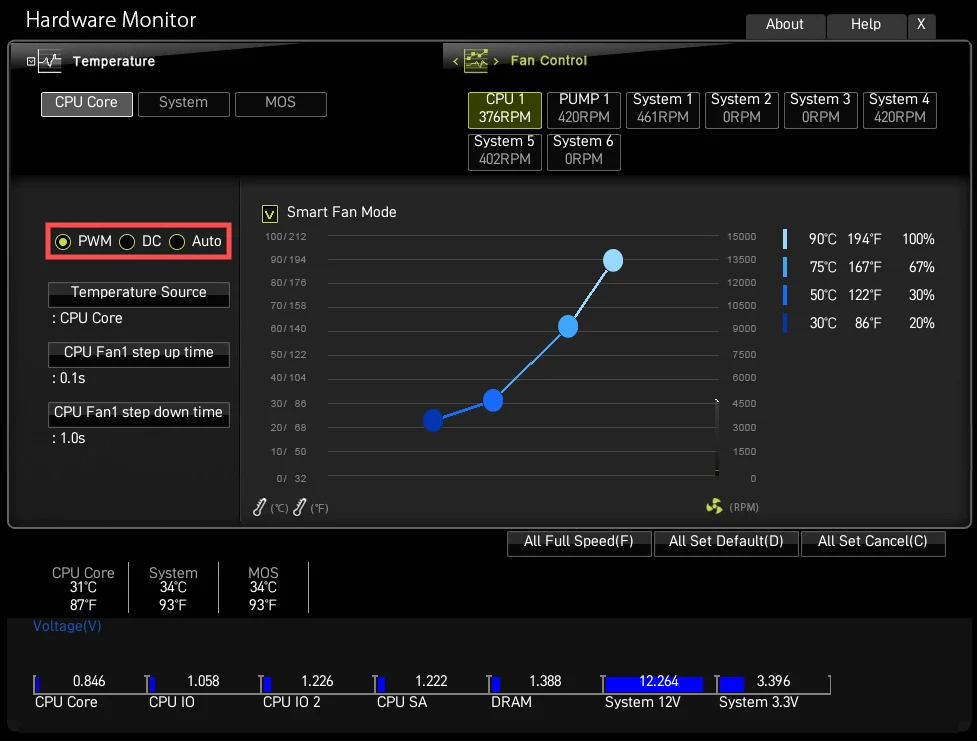
What Is the Ideal RPM for Everyday Use?
The ideal CPU fan RPM for everyday use is usually between 1,000 and 2,000 RPM. It depends on the size of the fan and your computer’s workload. For light tasks, a lower RPM is fine. If the CPU works hard, a higher RPM may be needed to keep the temperature low. Always check your computer’s cooling needs for the best RPM range.
What Is The Best RPM for Gaming?
The best RPM for gaming depends on your CPU and cooling system. Generally, a CPU fan running between 1500 to 2000 RPM during gaming provides good cooling. If your CPU gets hotter, it might need a higher RPM to prevent overheating. Ensure your fan speed is adjustable to balance cooling and noise. Always check the recommended fan settings for your specific CPU and keep it clean for better performance.
Read: Do I need To Reinstall Windows With New CPU – Explore For All the Details!
How Can You Check CPU Fan RPM?
BIOS/UEFI Settings: Restart your PC and open BIOS/UEFI to find fan speed settings.
Monitoring Software: Use tools like HWMonitor or SpeedFan to check RPM in real time.
Motherboard Software: Some motherboards have specific apps to monitor fan speed.
Fan Controller: Physical fan controllers display RPM directly.
Check Hardware: Some fans have RPM labels if the software isn’t available.
Can You Adjust the CPU Fan RPM?
Through BIOS Settings:
You can adjust the fan RPM through your computer’s BIOS. In BIOS, you can set the fan speed or create a custom fan profile based on temperature.
Using Software Tools:
Programs like MSI Afterburner or SpeedFan allow you to adjust fan RPM directly from your desktop. These tools provide a real-time view of temperature and fan speeds.
Automatic Adjustment:
Many modern motherboards automatically adjust fan speeds based on the CPU’s temperature. This helps your system stay cool without needing manual changes.
Fan Control Headers:
Some motherboards offer fan control headers. You can connect the fan to these headers and use software or BIOS to adjust the RPM.
External Fan Controllers:
If you prefer manual control, you can use an external fan controller. This device allows you to adjust fan speeds without using software or BIOS.
How Does Room Temperature Affect RPM?
Room temperature affects the CPU fan’s RPM because the fan adjusts its speed based on the system’s temperature. If the room is hot, the CPU heats up faster, causing the fan to work harder and spin at a higher RPM. In cooler environments, the fan operates at a lower RPM to maintain a stable temperature, reducing noise and energy usage.
What Happens If RPM Is Too Low?
If the RPM is too low, the CPU fan won’t be able to cool the system properly. This can lead to higher temperatures, causing the CPU to overheat and possibly damage the components. Lower RPMs may reduce noise but can also result in poor cooling performance.

What Happens If RPM Is Too High?
If the RPM is too high, the CPU fan will cool the system effectively but create more noise. Constantly running at high RPM may also cause the fan to wear out faster. High RPMs use more power and may not be necessary if the system is already cool enough.
Read: Very High CPU Load, But Nothing Significant In Top – Ultimate Guide 2024!
How To Balance Noise And Cooling With RPM?
To balance noise and cooling, adjust the RPM so that it’s fast enough to cool the CPU but not too fast to create unnecessary noise. Use software or BIOS settings to set a fan curve that increases RPM only when temperatures rise, keeping the fan quiet when the system is cool.
What RPM Is Suitable For Laptops?
Laptops generally use lower RPMs compared to desktop computers because they are designed for quieter operation. A typical laptop fan runs between 2,000 to 4,000 RPM, depending on the model and usage. Laptops prioritize cooling but also focus on maintaining low noise levels to improve user experience.
Is Higher RPM Always Better?
A higher RPM is not always better. While it can improve cooling, it can also lead to more noise and wear on the fan over time. It’s essential to find a balance where the fan speed is high enough to cool the system without producing unnecessary noise or reducing the fan’s lifespan.
What Tools Help Optimize CPU Fan RPM?
BIOS/UEFI Settings:
You can adjust the CPU fan RPM in the BIOS or UEFI of your computer. It lets you set fan profiles like silent, balanced, or performance to match your needs. Access it during startup by pressing a specific key like F2 or Delete.
Fan Control Software:
Software like SpeedFan or OpenHardwareMonitor allows you to control fan speeds directly from Windows. These tools show CPU temperature and adjust RPM based on system load.
Motherboard Fan Controllers:
Many motherboards have built-in fan control options. Using the manufacturer’s software or BIOS, you can adjust fan curves to increase RPM when the CPU gets hotter.
External Fan Controllers:
External controllers let you manage fan speeds manually. They connect to your PC and provide knobs or buttons to increase or decrease fan RPM easily.
Hardware Monitoring Tools:
Tools like HWMonitor or Core Temp monitor CPU temperatures. These tools help you understand if your current fan RPM is enough to cool your CPU properly and make adjustments if needed.
What Is The Impact Of Case Airflow On RPM?
Good case airflow helps your CPU fan work better at lower RPMs. When your PC case has good airflow, heat is removed more easily, allowing the fan to run at a lower speed. This can help reduce noise and still keep your CPU cool. Poor airflow makes the fan work harder, needing higher RPMs to cool down the system.
What Should Be The CPU Fan RPM?
The ideal CPU fan RPM depends on your usage. For general tasks, 1200 to 2000 RPM is fine. For gaming or heavy workloads, you might need 2000 to 3000 RPM to keep your CPU cool. Always monitor your CPU temperature to adjust the RPM as needed, ensuring efficient cooling without too much noise.
Read: Can I use 1150 CPU on 1151 motherboard – Need a New CPU? Click Here!
How Fast Should My CPU Fan Be Going?
Your CPU fan should run at a speed that matches your system’s needs. For normal tasks, 1200 to 2000 RPM is good. For gaming or video editing, you may need speeds of 2000 to 3000 RPM to keep the CPU temperature down. Always check your CPU temperature to decide the right fan speed for your tasks.
What RPM Is Good For Fans?
A good RPM for fans is typically between 1200 and 2000 RPM. This range offers a good balance between airflow and noise. For demanding tasks like gaming, the RPM may need to go up to 2500 or 3000 RPM to ensure your system stays cool but remember that higher RPMs can make more noise.
What is a good fan RPM for gaming?
For gaming, a fan RPM of 2000 to 3000 is ideal to maintain low temperatures. During intense gaming sessions, the CPU and GPU generate more heat, and higher RPM ensures enough airflow to cool them down. Be mindful of noise, as higher RPM fans can be louder, but they are necessary for better cooling during heavy use.
Is 2000 RPM good for a CPU fan?
Yes, 2000 RPM is good for a CPU fan, especially when running demanding applications like gaming or video editing. At 2000 RPM, your CPU will get enough cooling to prevent overheating. However, this speed can produce noticeable noise, so if noise is a concern, you may want to adjust based on your comfort level.
Is 1000 RPM good for a CPU fan?
A 1000 RPM fan may be good for light tasks like browsing or watching videos. However, if you’re running demanding programs or gaming, 1000 RPM might not provide enough cooling. You’ll likely need a higher RPM to keep the CPU cool and avoid overheating during heavy use. Always monitor your temperature to ensure it’s working efficiently.
Read: Can I Use 70 Alcohol To Clean CPU – Clean Your CPU Now!
Frequently Ask Questions:
1. What Is The Difference Between Low And High RPM For CPU Fans?
Low RPM means less noise but less cooling. High RPM increases cooling but can create more noise. High RPM is needed for demanding tasks, while low is enough for simple ones.
2. Can CPU Fan RPM Change Automatically?
Yes, many modern CPU fans change RPM based on the temperature. As the CPU heats, the fan RPM increases to cool it down and lowers when the temperature drops.
3. What RPM Is Too Low For A CPU Fan?
Anything below 1000 RPM is typically too low for most systems, as it may not provide enough airflow to cool the CPU, especially during heavy tasks like gaming.
4. Does RPM Affect CPU Performance?
RPM itself doesn’t directly affect CPU performance, but insufficient fan RPM can lead to overheating, which can cause the CPU to throttle its performance to prevent damage.
5. How Do I Know If My CPU Fan RPM Is Too High?
If your CPU fan RPM is too high, it may cause noticeable noise and vibration. Check your system’s temperature—if the CPU is too cool and the fan is loud, it may be too high.
6. Are There CPU Fans With Fixed RPM?
Yes, some older or basic CPU fans have fixed RPMs. These fans do not adjust based on the CPU temperature and are less efficient in cooling for varying workloads.
7. How Does Dust Affect CPU Fan RPM?
Dust can clog the fan blades and decrease airflow, causing the fan to work harder. This may lead to higher RPM and potentially more noise as the system struggles to cool the CPU.
8. Can A Noisy Fan Mean The RPM Is Too High?
Yes, if the fan is too noisy, it may be running at a high RPM. This often happens when the CPU is hot, but it can also mean the fan is inefficient.
9. What RPM Should I Use For Overclocking?
When overclocking, you may need higher RPMs (2000-3000 RPM) to ensure the CPU stays cool. Overclocking increases heat, so better cooling is necessary to maintain performance and stability.
10. Does The Size Of The Fan Affect The Needed RPM?
Yes, larger fans can move more air at lower RPMs, reducing noise. Smaller fans need higher RPM to push the same amount of air, often creating more noise at higher speeds.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, choosing the right RPM for your CPU fan is important for keeping your system cool and running smoothly. For everyday tasks, a range of 1000-2000 RPM is ideal. For gaming or heavy work, 2000-3000 RPM may be necessary. Always check your CPU temperature to ensure your fan is working efficiently and adjust the RPM accordingly for optimal cooling.
Related Posts:
- CPU Machine Check Architecture Error Dump – Fix Hardware Issues!
- Corespotlightd High CPU – A Complete Guide _2024!
- Is 80 Degrees Celsius Hot For A CPU – Check CPU Temperature Now!
- B550 Gaming Plus CPU Light On – Fix B550 CPU Light Now!
